Fixing Printer Wi-Fi Issues—Fast and Simple
It’s a scenario all too familiar—your printer was working just fine yesterday, and today it’s suddenly offline, unable to connect to Wi-Fi. Whether you’re printing documents for work, school assignments, or personal projects, a disconnected printer can bring everything to a halt. Understanding the reasons behind this frustrating issue is the first step toward a reliable fix.
Quick Navigations
- 1 1. Common Culprits: What Breaks the Connection?
- 2 2. Understanding Wi-Fi Connectivity in Printers
- 3 3. The Role of Firmware and Driver Updates
- 4 4. Printer Placement and Environmental Factors
- 5 5. Router and Network Configuration Issues
- 6 6. IP Address Conflicts and DHCP Challenges
- 7 7. Printer Sleep and Power-Saving Settings
- 8 8. Firewall, Antivirus, and Network Security Protocols
- 9 9. Troubleshooting Steps: A Practical Checklist
- 10 10. Brand-Specific Solutions and Tools
- 11 11. When to Call for Professional Help
- 12 12. Preventive Tips for Long-Term Connectivity
- 13 Conclusion: Stay Connected with Confidence
1. Common Culprits: What Breaks the Connection?
When your printer suddenly refuses to cooperate, it’s usually due to one of the following:
- Wi-Fi Signal Interference: Walls, appliances, or neighboring networks can disrupt connectivity.
- Printer Firmware Glitches: Outdated software may fail to support current Wi-Fi standards.
- Network Configuration Changes: Router resets, password updates, or SSID renaming can knock devices offline.
- IP Address Conflicts: Static IP settings may clash with your current network.
Top 5 Common Reasons
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Weak Wi-Fi Signal | Distance from router or physical obstructions |
| Incorrect Network Credentials | Wrong Wi-Fi password or SSID |
| Router Issues | Overloaded or outdated router firmware |
| Printer Sleep Mode | Power-saving settings interrupt connectivity |
| Firewall/Antivirus | Overprotective settings blocking printer access |
2. Understanding Wi-Fi Connectivity in Printers
How Printers Connect to Wireless Networks
Most modern printers use either:
- Wi-Fi Direct: Printer creates its own network for direct connections.
- Infrastructure Mode: Printer connects to your home or office router.
These connections depend heavily on consistent signal strength, proper authentication, and seamless communication between devices.
Network Bands Matter
- 2.4GHz Band: Longer range, lower speed.
- 5GHz Band: Higher speed, shorter range.
Many printers only support 2.4GHz. Connecting to a 5GHz-only network may lead to issues.
3. The Role of Firmware and Driver Updates
Outdated firmware is one of the most overlooked causes of Wi-Fi disruptions.
Why Updates Matter
- Fix known bugs affecting connectivity.
- Improve security protocols.
- Optimize compatibility with newer routers and devices.
How to Check for Updates
- Visit your printer brand’s official support page.
- Use bundled software like HP Smart, Epson Software Updater, or Canon IJ Utility.
- Navigate via the printer’s touchscreen to firmware update settings.
4. Printer Placement and Environmental Factors
Where your printer lives can significantly affect its ability to maintain a wireless connection.
Avoid These Printer Placement Mistakes
- Near metal furniture or filing cabinets that reflect signals.
- Too far from the router (more than 30-50 feet, depending on the layout).
- Surrounded by microwave ovens, cordless phones, or baby monitors (all create interference).
Best Practices for Optimal Placement
- Keep within line-of-sight of the router when possible.
- Elevate the printer slightly for better signal reception.
- Avoid tight corners or closets.
5. Router and Network Configuration Issues
Sometimes the problem lies not with the printer, but with your network itself.
Watch for These Red Flags
- SSID Changes: If you recently renamed your Wi-Fi, the printer won’t auto-detect it.
- Password Updates: Must be manually re-entered on the printer’s control panel.
- MAC Filtering Enabled: Printer’s MAC address must be whitelisted.
- Router Reboots or Power Surges: Can reset connections or IP settings.
Router Best Practices
- Assign a static IP to your printer via router settings.
- Disable guest networks for printers—stick to the main SSID.
- Use WPA2 security (WPA3 if compatible).
6. IP Address Conflicts and DHCP Challenges
Each device on your network must have a unique IP address. When DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) gets confused, it can assign duplicate or unstable addresses.
Symptoms of IP Conflicts
- Printer shows as “offline” despite being on the network.
- Repeated drops during print jobs.
- Printing works intermittently.
Solutions
- Set a static IP for the printer via your router or printer control panel.
- Restart both your printer and router.
- Limit the DHCP range in your router to prevent overlapping addresses.
7. Printer Sleep and Power-Saving Settings
How Power Modes Interfere
- Many printers enter deep sleep to conserve power.
- This can disable the network adapter or Wi-Fi antenna temporarily.
What to Do
- Disable aggressive power-saving settings.
- Schedule printer wake-up times.
- Enable “Always-On” network mode (if supported).
8. Firewall, Antivirus, and Network Security Protocols
Security software on your computer or router can sometimes block legitimate device communications.
Firewall-Related Printer Issues
- Cannot detect printer on the network.
- Print jobs get stuck in the queue.
- Network scanning features disabled.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Temporarily disable firewall or antivirus to test connectivity.
- Create a firewall exception for your printer’s IP or software.
- Use trusted home networks—avoid public Wi-Fi for printer setup.
9. Troubleshooting Steps: A Practical Checklist
Here’s a methodical approach to resolve most Wi-Fi printer issues:
- Restart Everything: Printer, router, and computer.
- Check Connection: Is the printer connected to the correct SSID?
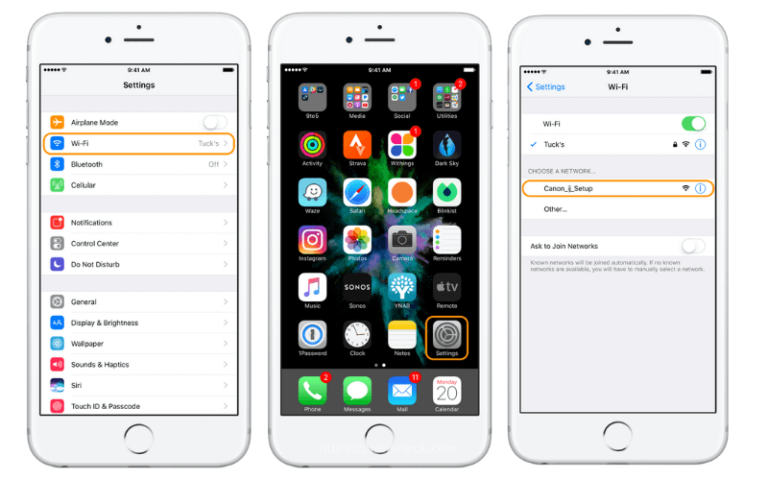
- Reconnect Printer to Wi-Fi: Manually enter the SSID and password.
- Update Drivers/Firmware: Download the latest from manufacturer’s website.
- Print Network Report: Many printers offer diagnostic reports from the settings menu.
- Assign Static IP: Use the router’s admin interface.
- Disable Firewall Temporarily: Especially for setup or first connection.
- Reinstall Printer Software: Use official setup tools for best results.
- Try USB Setup First: Then enable Wi-Fi post-installation.
10. Brand-Specific Solutions and Tools
HP Printers
- Use HP Print and Scan Doctor tool.
- Check for Wi-Fi Direct toggle conflicts.
Epson Printers
- Reset network settings via control panel.
- Use Epson Connect Utility for remote management.
Canon Printers
- Utilize Canon IJ Network Tool.
- Some models require a WPS (push button) router setup.
11. When to Call for Professional Help
If you’ve tried every step and the printer still won’t connect:
- Hardware Failure: Internal Wi-Fi chip may be damaged.
- Router Firmware Issue: Advanced troubleshooting may be needed.
- Business-Critical Printing: IT intervention is recommended for networked printers in offices.
12. Preventive Tips for Long-Term Connectivity
Maintenance is Key
- Schedule firmware checks monthly.
- Keep your router in a clean, ventilated location.
- Avoid unnecessary SSID or password changes.
Smart Home Integration
- Enable cloud printing or email-to-print features.
- Use apps like Google Cloud Print (legacy), HP Smart, or Epson Email Print.
Conclusion: Stay Connected with Confidence
Printers are essential tools—but their dependence on Wi-Fi makes them vulnerable to an array of technical hiccups. From firmware updates and router settings to physical placement and security protocols, even the smallest details can lead to major disruptions. The good news? Armed with the right knowledge and a step-by-step approach, you can troubleshoot confidently and get your printer back online—where it belongs.